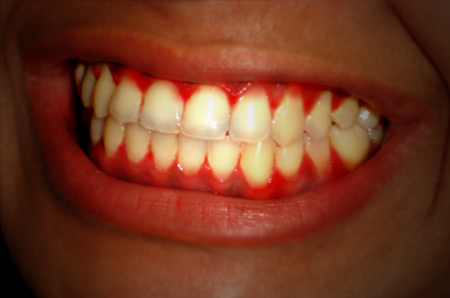
Most people have experienced gum bleeding sometime or the other in their lives. The condition can occur chronically for many days, or be a short term problem, depending on the cause. Mostly it is noticed during brushing of the teeth, or patients may complain of bleeding of gums after slightest injury to the gums or after only touching or sucking their gums. There generally is a presence of red, tender or swollen gums. Difficulty and discomfort in mastication and food intake occasionally due to pain and sensitiveness may also be experienced, but rarely. Here’s an insight into gingival bleeding and the ways in which it can be treated.
Why do gums bleed?
There can be numerous reasons for gingival bleeding. The more common reasons for bleeding gums can be presence of plaque (soft yellowish deposits on the teeth), and/or tartar (the hard yellowish white or brown deposits on the teeth that cannot be removed easily), or stains, or even injury due to excessive flossing of the teeth. But sometimes, it can even be a sign of a more serious condition, disease or disorder. When present, plaque, tartar or stains contain millions of bacteria which produce irritants, leading to inflammation of the gums. This inflammation (gingivitis) makes the gums more spongy, swollen, soft and susceptible to bleeding as it makes the gums weaker. This is the most common reason for gingival bleeding.
However, other reasons which may be responsible are:–
Inappropriate flossing technique, tooth picking, a blow and similar other factors may impair or traumatize gums. Sometimes certain drug interactions may also cause gum bleeding as a side effect. It may result as a side effect of taking aspirin, heparin therapy, pain killer, chemotherapy which are blood thinners. Mostly warfarin interactions with other drugs cause gums to bleed. Other dental conditions like gum diseases, trench mouth, poorly made restorations, etc. Serious medical conditions such as clotting disorders, leukemia, deficiencies of vitamins C and K may cause persistent gum bleeding. Pregnancy is another condition where gum bleeding can be experienced.
Why is prevention important?
Gum disease and not tooth decay is the most common cause of tooth loss. If present, gum disease can invade the tissues around the tooth root (gums and bone) to loosen the tooth, and finally shed the tooth. Hence, to keep our teeth healthy for life, it is very important to maintain healthy gums. Numerous studies have proven a strong link between cardiac disease and bleeding gums. Gum disease reportedly reduces the health of the tissues lining the gum, rendering it simpler for the bacteria causing gum disease or that are present in the oral cavity to enter the bloodstream through injured blood vessels which run through the gums. This increases the toxin level in the blood, which results in the increased risk of stroke, stomach ulcers, lung infections, pneumonia, low birth weight babies and premature delivery.
Studies have shown that the most predominant bacterial species, Streptococcus sanguis causes the clumping of blood platelets, which develops into a blood clot. If this blood clot is detached and is mobile, it can clog an important artery to cause a heart attack. Also, patients with gum disease also known as periodontitis have significantly higher levels of inflammatory products for e.g. fibrinogen and white blood cells which are well known risk factors for acute heart attacks.
The diagnosis of gum bleeding and hence its treatment may get delayed or be missed since it is less often severe and does not need immediate medical attention. But as it can be a manifestation for many different medical conditions, it is very important not to overlook bleeding gums and hence, its treatment.
Ways of Prevention and Home Care:
The first and most important and effective preventive measure is maintaining oral and dental hygiene. A proper brushing technique is the key here. We must brush teeth gently with a soft-bristle toothbrush after every meal. Obviously, there are different ways of brushing, and likewise, different types of toothbrushes. It is wise to ask your dentist what would suit you best. You may be recommended salt water rinsing or prescribed mouthwashes. Avoid using excessive commercial, alcohol-containing mouthwashes, which can result in unwanted effects. Also, flossing teeth twice a day can prevent plaque from building up between the teeth. And, plaque formation can be reduced by avoiding snacking between meals, esp. carbohydrate rich foods.
Visit the dentist at least once every 6 months for tartar removal while following your dentist’s home care instructions. Chlorhexidine mouthwashes seem to effectively reduce plaque and gingivitis. Chlorhexidine reduce bacteria present in the mouth to harmless levels. However, again, there may be drawbacks to the use of chlorhexidine with chronic use possibly producing brownish stains on the teeth which are difficult to remove. A change in taste can be also be experienced as a side effect. It is also contraindicated for women who are pregnant or nursing. Listerine, a therapeutic antiseptic mouthwash can also be used. It is less effective in comparison with chlorhexidine, but it contains phenolic compounds and essential oils.
Use of poorly fitting dentures cause sore spots in gums causing bleeding, this can be corrected by relining or modification of the dentures by the dentist. Furthermore, aspirin must be avoided unless it has been recommended to you by your healthcare provider. Bleeding gums caused due to deficiency of vitamins can be reversed by intake of the required vitamins. If you have a habit of sucking your gums, then it must be stopped. When plaque that is present on the teeth, hardens over a period of time, it will be necessary for a dental professional to remove it from teeth with the help of special equipment, because it does not come off with regular brushing or flossing techniques.
If you have been taking care of your teeth and gums regularly, inspite of which you have ended up with gum bleeding, then you might need special treatment with a type of antibiotic. This will be prescribed by the dentist after a thorough checkup.
General Treatment of Bleeding Gums:
Some people do have very sensitive gums, and special brushes and toothpastes help. Chronic use of tobacco products must be avoided, as this aggravates bleeding gums. If injury or trauma is the cause of the bleeding, it can be controlled by applying pressure directly with a gauze pad soaked in cold water. If you have been diagnosed with a vitamin deficiency, take recommended vitamin supplements, as prescribed by your doctor. Avoid aspirin, unless it has been prescribed or recommended for you. Using an oral irrigation device which is mainly used to massage the gums can be an optional additional measure to keep gums healthy. Gum disease most often doesn’t hurt. You may have it for years before you feel discomfort but you needn’t wait for the pain to seek treatment.
If the bleeding is severe or long term (chronic), medical intervention is required. So also if your gums continue to bleed even after treatment or you have other unexplained symptoms with the bleeding related to dental or other body systems.
Finally: We must remember to brush regularly to avoid complications of the gums, which may finally lead to tooth loss. Hence it is very important to take good care of your teeth by maintaining proper oral hygiene regularly.
– Dr. Ritu B. Kulkarni